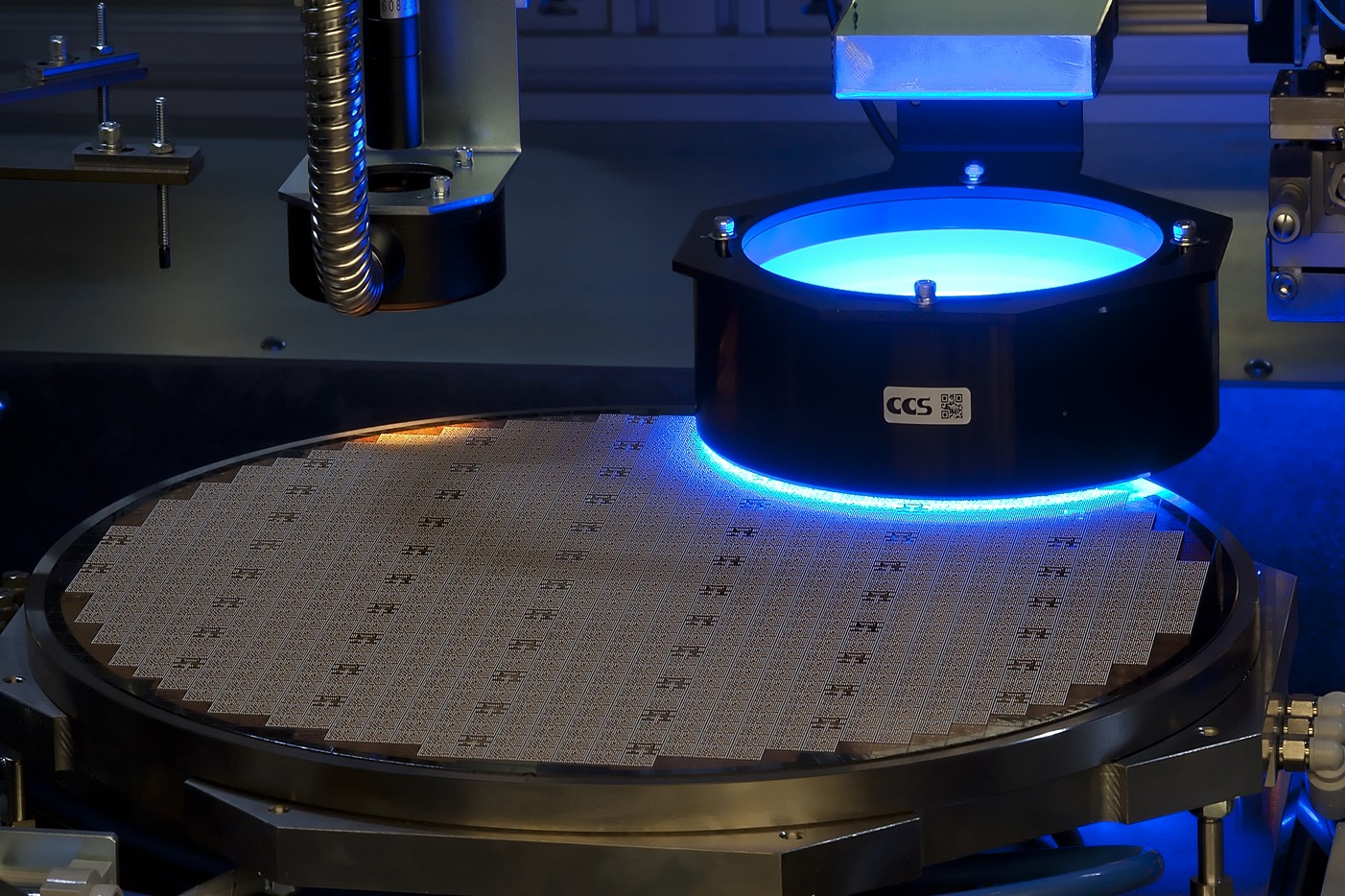
Smart and Sustainable Manufacturing
BLUMORPHO is committed to tackle climate change, resource depletion, and costs in manufacturing and industrial processes. We believe that cross-sectorial and multi-player collaborations are essential to drive progress and develop new business models that prioritize sustainability for everyone involved.

Smart and Sustainable
Manufacturing

We believe that cross-sectorial and multi-player collaborations are essential to drive progress and develop new business models that prioritize sustainability for everyone involved.
Shape the Future of Smart Manufacturing and Semiconductors with Us
Discover how innovation, sustainability, and technology are transforming industries. Watch our expert-led discussions and explore the opportunities that await in Smart Manufacturing and semiconductors.
Advanced Packaging: Pioneering Europe's Semiconductor Manufacturing
Explore how advanced packaging technologies are revolutionizing semiconductor manufacturing in Europe. By integrating chiplet architectures and 2.5D/3D integration, these innovations enhance performance, reduce development costs, and address the limitations of traditional system-on-chip designs. At BLUMORPHO, we are committed to driving sustainability and innovation in the semiconductor industry through collaborative efforts and cutting-edge solutions.
European Strategies for Semiconductor Sustainability
Hind Beaujon, Jean-Christophe Eloy, and Nicolas Leterier
discuss European strategies to strengthen sustainability within the semiconductor industry. They explore ongoing and future initiatives to integrate sustainable practices across the semiconductor value chain in Europe.
Global Comparison of Sustainability in the Semiconductor Industry
Nicolas Leterier from Schneider Electric
analyzes global sustainability efforts in the semiconductor industry. He highlights regional differences in sustainable practices and emphasizes areas where improvements are necessary to achieve worldwide sustainability goals.
ESG goals
With the increasing concerns about climate change, resource depletion, and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, governments, corporations, and consumers alike are seeking ways to reduce their environmental impact, and the manufacturing sector is no exception. The manufacturing industry is enduring crisis after crisis, and is facing a workforce shortage with younger generations losing interest for careers in the manufacturing sector. Is the emerging regulation on ESG goals another burden or an opportunity?
In the recent years, Europe has been leading the way in the development of regulations aimed at promoting ESG goals for manufacturing companies. The regulatory changes will apply to large companies at first. But the reporting on the carbon emission in the frame of the scope 3 will technically affect the supply chain and we can expect smaller companies to report for their customers.
This is a virtuous process, since by integrating ESG goals principles into their operations and decision-making processes, manufacturing companies can improve their overall performance and reputation while contributing to a more sustainable and equitable future.
Energy savings and energy sources are essential in this framework, but other technologies and concepts can generate a true multiplying effect.
Micro Factories
The COVID crisis has demonstrated the fragility of the supply chain and the limitations of a system in permanent tension with “just-in-time” pushed to the limit. More and more companies started to reflect on how they could change their sourcing with partners located closer delivering faster with reduced transportation cost.
Micro factories are designed to be flexible and adaptable, allowing manufacturers to quickly switch between different products and production processes based on changing customer demands. This agility is made possible by the use of advanced automation and digital technologies (discover our open discussion with the entrepreneur Jacques Weyn about the digitalisation of the manufacturing industry), such as robotics, artificial intelligence, 3D printing and IoT. Micro Factories are helping to create more sustainable and resilient supply chains, while also enabling greater innovation and customization in product design.
Decentralised production
Human centric technologies
Drivers Behind the Emerging Sustainability Investment Trend
François Tison from 360 Capital
explores the factors fueling the rising trend of investment in sustainable initiatives. He discusses why investors are increasingly supporting projects that combine profitability with a positive environmental impact, especially in Smart Manufacturing.
Opportunities for European Startups in Manufacturing
Nicolas Topuz from Supernova Invest
examines opportunities available to European startups in the manufacturing sector. He addresses the challenges startups face and offers strategies to leverage current trends in technology and sustainability.
“The manufacturing industry must reinvent itself and perform a real transition. Digitalisation alone will not be sufficient; the adoption of advanced technologies must not only aim at the optimization of processes but also minimize their environmental and social impact. This smart and sustainable approach to manufacturing aims to achieve maximum efficiency and productivity while optimizing the use of resources, reducing wastes, monitoring and reducing the carbon footprint and addressing the talent shortage in industry.”
Regis HAMELIN
BLUMORPHO CTO

Perspectives on the Future of Manufacturing in Europe
Aurore Lanchart from OSS Ventures
shares her vision for the future of the manufacturing sector in Europe. She discusses expected developments, such as the increased integration of smart technologies and sustainable practices, and how companies can prepare for these changes.
Hopes for the Future of Manufacturing
Hind Beaujon from Pfeiffer
expresses her aspirations for the future of the manufacturing industry. She highlights the importance of innovation, collaboration, and the adoption of sustainable practices to ensure the long-term competitiveness and resilience of the sector.
Unlocking AI’s Potential in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Explore our discussion with FESTO on how AI is transforming semiconductor manufacturing. Learn key strategies to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and optimize resources.
At BLUMORPHO, we foster innovation through cross-sector collaborations to drive sustainability in the industry.
To Go Further
Dive deeper into innovation and expertise to explore new opportunities.
Advanced Packaging in Europe's Semiconductor Ecosystem
The semiconductor industry is undergoing a pivotal transformation.
Discover The Blumorpho Experts Team
Meet Regis Hamelin
Blumorpho CTO & Deep Tech Expert
Experts Perspectives
Venture-Capital speak out

3:35

2:12

1:06

1:43

0:47